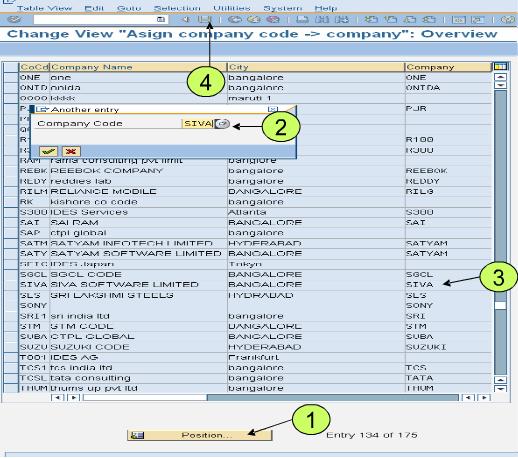
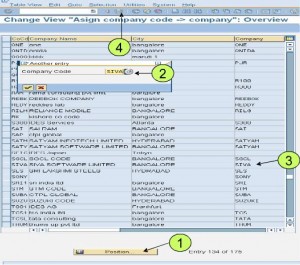
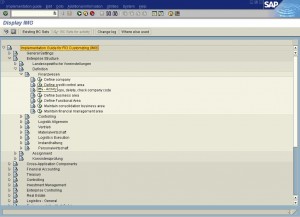
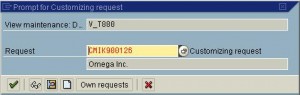
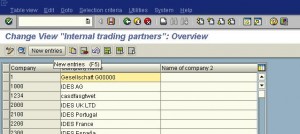
A financial year is termed as a fiscal year. A fiscal year may or may not be the calendar year depending on the country. Fiscal year variants defined in SAP are:
- V3 – April to March
- K4 – January to December
- V6 – July to June
- V9 – October to September