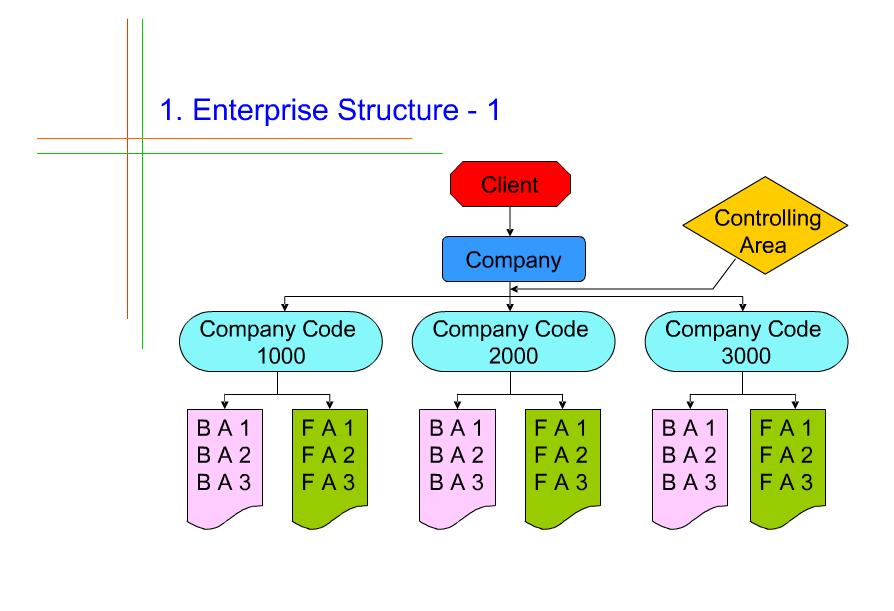
Fiscal year variants in SAP
A financial year is termed as a fiscal year. A fiscal year may or may not be the calendar year depending on the country. Fiscal year variants defined in SAP are:
- V3 – April to March
- K4 – January to December
- V6 – July to June
- V9 – October to September
Business Area – OX03
Define Enterprise Structure – Steps
- Define companies (define a company)
- Define Company codes (What is a company code?, Link1Link2, Define company code Global parameters)
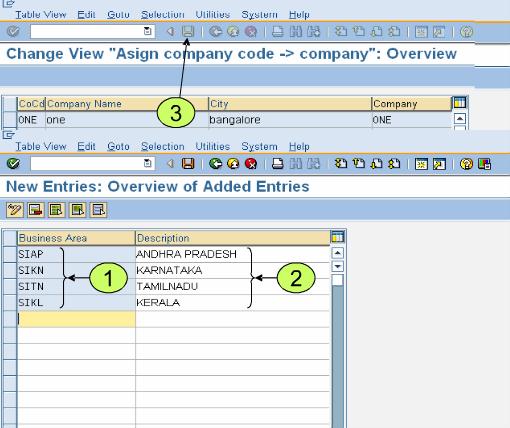
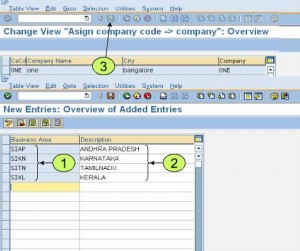
- Assign company codes to companies (Assign company codes to companies)
- Define business area
- Define functional area
- Define credit controlling area
- Assign business area, functional area, credit controlling area to company codes
Company and Company Code configuration
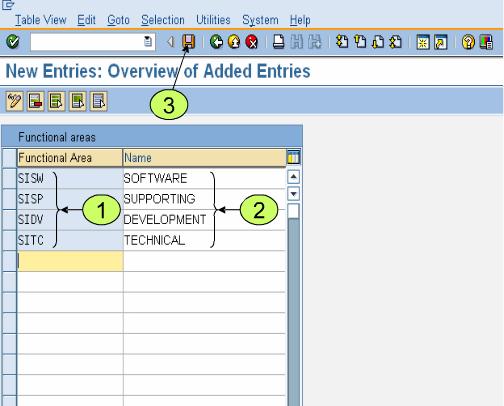
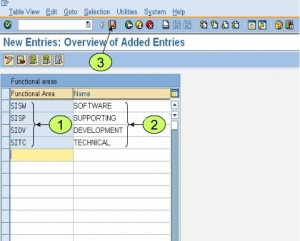
Maintain Functional Areas – OKBD
Functional Areas within the FI Enterprise structure are used to organize your business for cost of sales (COS) accounting. Functional areas allow you to segregate and classify different types of costs within one expense account. This makes it possible for example, to use a single labor account to determine what amount of labor is spent directly on production as opposed to sales or administration. It is possible to report on functional areas from both FI and Profit Center Accounting.
Enterprise Structure >> Maintain Structure >> Definition >> Financial Accounting >> Maintain Functional Areas
Transaction code: OKBD
Saks Apparel has determined that it requires five functional areas to classify cost of sales accounting. The functional areas are Administration, Sales, Production, Research & Development and Marketing. By using these functional areas, Saks Apparel will be able to report on an individual expense account using these five categories. Our next piece of configuration will be able to enable SAP to populate our postings with functional areas.
Business Areas – OX03
FICO Configuration Series – Part 9
Define Business Areas (click here for short version with screenshots)
Enterprise Structure >> Maintain Structure >> Financial Accounting >> Maintain Business Area
Transaction code: OX03
The function of a business area is to create balance sheets and profit and loss statements below the company code level. Some common uses of business are to produce divisional financial statements or SEC segment-level reporting. It is important to note that business area functionality can be duplicated using profit center accounting. The decision to use or not to use business areas should be made early on in the design phase of your project. Many new projects are leaning away from business areas and towards profit centers, but ultimately, the decision is an individual project decision based on what fits in the overall system design of the project implementation. Some of the deciding factors are the need to report business lines across company codes, the need for full balance sheets at the divisional or business line level, as well as the cost and the benefits of business areas versus profit centers.
Business areas are independent of any other FI enterprise structure. Therefore, business areas are designed to cut across company codes. A common mistake that some companies make is to force one-to-one relationship defeats the entire purpose of business areas. The purpose of business areas is to be able to report on similar activities that occur across company codes. There is no residual benefit to configuring business areas in that manner. As a matter of fact, it often causes a lot of reconciliation problems because business areas are not linked to company codes in standard configuration.
In this screen enter Alphanumeric identifier for the business (up to 4 char) are and description
Saks Apparel has decided to use three business areas. The CFO has determined that he would like a cross-company balance sheet for both the apparel and textile industries in which Saks Apparel conducts business activity. In order to better track non-value-added administrative assets and expenses, the services business area was created. The new shared services department that provides centralized administration functions for the organization is being implemented as part of the business process reengineering effort portion of the SAP project implementation. It is important to remember that the idea is for all company codes to share all the business process reengineering effort portion of the SAP project implementation. It is important to remember that the idea is for all company codes to share all the business areas. The one exception is that the accounting department wants to ensure that postings one particular company code are only posted to one particular business area.
Although Business Areas are not linked to any other FI Enterprise Structures, they can be linked to other organizational elements in the system. Some of them are listed below:
|
Enterprise Structure |
Why is this linked to the Business Area? |
|
Plant/Valuation Area & Division |
Very useful to link Business area to plant/valuation area and division because single plants usually produce products for one Business Area |
|
Plant & Division |
Similar to previous. The decision whether to link or not is taken by the MM team |
|
Sales Area |
In sales organizations which sell a single grouping of products, business areas are linked to sales areas to ensure revenue postings are made to correct business area |
|
Cost Centers |
Sometimes, it makes sense to map business areas to cost center |
|
Assets |
In the company code, if the Business Area Balance Sheet indicator is enabled, business area becomes a required field fixed asset class module |
|
Consolidation Business Areas |
Consolidate business areas for reporting purpose |
Define Parallel Currencies – OB22
FICO Configuration Series – Part 8
Define Parallel Currencies
Financial Accounting >> Financial Accounting Global Settings >> Company Code>> Parallel Currencies >> Define additional local currencies
Transaction Code: OB22
Company Code: Enter the four-digit identifier of the company code that you wish to configure.
1st Local Currency: These fields will fill in automatically with default information based on the currency defined in the company code definition.
2nd and 3rd Local Currency: As explained earlier, each company code can have two additional parallel currencies that can be used in conjunction with local currency defined for the company code
Curr. type: The currency type field specifies which type of parallel currency you want to configure. The following options are available.
Group Currency: Group currencies are defined at the client level in table T000. Group currencies are used to enable cross-company postings in controlling for company codes that use different company code currencies.
Hard Currency: Hard currencies are used for subsidiaries in countries with a lot of inflation. Hard currencies allow you to better valuate transactions in an inflationary economic environment.
Index-Based Currency: Index-based currencies are used for statutory reporting purposes for subsidiaries in some countries that have extreme amount of inflation.
Ex. Rt. Type: The exchange rate type determines how foreign currencies are revalued at the time of foreign currency revaluation and translation. The number of possible entries is too numerous to list here J
Srce Curr: Enter the source currency that the foreign currency is to be translated against. The possible entries are as follows:
Translation taking transaction currency as basis: This option always tries to translate the parallel current against the transaction currency of the document.
Translation Taking First Local Currency as Basis: This option always translates the parallel currency against the first local currency (company code currency).
TrsDte Typ: This setting is used to determine which date is used for foreign currency translations. The available options are as follows:
1. Document Date: Select this option if you want the translation calculation to use the exchange rate that was In effect on the day the document was dated.
2. Posting Date: Select this option if you want the translation calculation to use the exchange rate that was in effect on the posting date in the document.
3. Translation Date: Select this option if you want the translation calculation to use the exchange rate that is in effect on the date of the foreign currency translation.
Saks Apparel has decided to use a hard currency to help offset the inflationary pressures of its Mexican based company code. US dollars are used as hard currency. The peso is the company code currency for the Mexican division. Saks Apparel has decided to use the transaction currency as the base currency for translation and to use translation date to determine proper exchange rate. Because we have company codes with different currencies using the same controlling area, we also configured a group currency of US dollars for all company codes. The group currency will allow us to make cross company code postings in the controlling module. We will also need to make entries for all of the US company codes to add the group currencies to their records.
Define Countries – OY01
FICO Configuration Series – Part 7
Define Countries
Global Settings >> Set Countries >> Define Countries
Transaction Code: OY01
In the first screen, you need to select the country (MX) – the next screen that pops up will require the following details:
Hard Currency: Enter the key of you want to set as hard currency for the country. Hard currencies are used in countries with high inflation to improve the value of the transactions. When a hard currency is selected, the document is automatically updated in the local currency and the hard currency.
Index-Based Currency: Index currencies are used for statutory purposes in some countries with very high inflation. The way index currency valuation reporting works depends on the rules of each specific country. Enter the key of the currency that you want to set as index currency, if applicable, for your country.
Date Format:
Enter Date preference. Also keep in mind whether Europeans may use the same database at some future time.
Decimal Format:
Decimals using periods or commas. Also keep in mind whether Europeans may use the same database at some future time.
Although hard currency has been configured at country level, to activate this feature, hard currency needs to be configured at the company code level be defining parallel currencies.