All Materials in SAP have a material master and material master is the heart of all integration.
How To Use SAP FI Module
Five previous IBM workers in Mannheim, Germany were the 1st ones to start SAP or Applications and Products in 1972. It is the biggest inter-enterprise software company in the universe. It was a different idea from SAP to provide customers the capability to process unitedly with a ordinary corporate database for massive ranging applications. As a matter of fact a amount of big organisations like IBM and Microsoft are taking the help of SAP products today, for the easy working of their business.
SAP applications have been set up around the R/3 system, which makes it efficient to handle production operations and materials, financial and cost accounting, personnel and other archived documents. SAP in plain words is a answer for planning the resource of the corporation by taking the several procedures of the corporation unitedly.
A fresh package has been established explicitly for financial issue acknowledged as SAP FI module. It has been projected specifically to see comprehensive accounting and financial requirement of the business. The financial situation of a company can be evaluated by the financial managers of the enterprise in existing time with the assistance of this module. With the facility open by the procedures of the SAP FI modules, it is attend the financial managing director to come up with decisions which are more positive for the company and they can also make estimated programmes. The SAP FI module has the capacity to amalgamate with different facets of the corporation like human resource, materials management, sales, production planning and different vital modules.
There are numerous main requirements which the company has to see if they plan to acquire the help of this SAP module. A structure has to be planned in the organization which has to be managed well by the several coaches. This structure is developed by taking the organization, client, business region configurations in mind. The client unit is the top unit in a SAP system and it has every essential and legal records including the tables.
In Fact there are a number of sub modules of the SAP FI Module and are taken into use as per the essential of the enterprise. These can be named as:
Travel Management
Accounts Payable
Funds Management
Special Purpose Ledger
Asset Accounting
General Ledger
Accounts Receivables
Bank Accounting
Consolidation
There is no doubt that putting SAP into service is an pricey suggestion. But then the rewards far outweigh the money which you spend on this. This makes the task of every of your coaches much easier and the time they save is money gained for your company. As a matter of fact you can redeem a great deal more than you always thought. Testimonials of the customers who are using the different applications of SAP including SAP FI modules will validate the truth. It is possible to negotiate the price with SAP and it too counts on whatsoever things like the number of individuals who will utilize etc.
SAP is famous among the people who use it as a wholly integrated system. You should study about all the tips of integration in the new SAP FI Module to be able to manage the software good enough. The units of company are much easier classified in SAP FI Module compared to the other SAP modules.
SAP Internal Order Configuration – Screenshots
The Steps for Internal Order configuration are:
-
Organizational Structure
-
Order Master Data
-
Planning
-
Settlement
Internal Order – Introduction
Let’s say in an organization there are various events such as trade fairs, training seminars, which occur during the year. Now let’s assume for a second that these Trade fairs are organized by the Marketing cost center of the organization. Therefore in this case marketing cost center is responsible for all the trade fairs costs. All these trade fairs costs are posted to the marketing cost centers.
Now if the management wants an analysis of the cost incurred for each of the trade fair organized by the marketing cost center how would the marketing manager get this piece of information across to them?
Now this is where Internal Order steps in .If you go through all cost center reports this information is not readily available since all the costs are posted to the cost center.
SAP, therefore provides the facility of using internal orders which comes in real handy in such situations. In the above scenario the controlling department would then need to create an internal order for each of the trade fair organized. The cost incurred for each of the trade fair will be posted to the internal orders during the month. At the month end, these costs which are collected in the internal order will be settled from these orders to the marketing cost center. Thus the controlling person is now in a position to analyze the cost for each of the trade fair separately.
Thus internal order is used to monitor costs for short term events, activities. It helps in providing more information than that is provided on the cost centers. It can be widely used for various purposes . If used intelligently it is a real handy tool. Thus Internal order is basically a cost object which is used to monitor cost of a time restricted job. There are various types of internal order the common ones being a Real order where you collect costs and settle it at the month end. Ther others are statistical orders and we also have capital orders for capital projects
Functional Area Substitution – GGB1
In order to populate your postings with functional areas, you must setup a substitution. Substitutions are similar to validations. Unlike validations that create on-screen messages to the user, substitutions actually replace and fill in field values behind the scenes without the user’s knowledge. Similar to validations, substitutions can be setup for a number of different application areas and callup points. Substitutions are activated on the company code level, so it is important to ensure that you have followed all steps for each company code.
Financial Accounting >> Special Purpose Ledger >> Tools >> Maintain Validation/Substitution/Rules >> Maintain Substitution
Transaction code: GGB1
The fields in Create Substitution screen are:
Application Area: Enter the appropriate area is the module or submodule that you wish to create the substitution for. The available options are:
AM Asset Management
CO Controlling
FI Financial Accounting
GL Special Ledger
JV Joint Venture Accounting
KC Enterprise Controlling – SAP EIS
PC Profit Center Accounting
PS Project Systems
Callup Point: Callup points determine when the substitution is run. For FI application area, the following callup points are available
0001 Document header: Use this callup point to substitute entires at the document header level. The entries that are usually available substitution at this point are stored in the BKPF table.
0002 Line Item: Use this callup point to substitute line item entries within a document. The entries that are usually available for substitution at this point are stored in BSEG table.
0003 Complete Document: This callup point substitutes settings for the document as a whole. This activity is also known as matrix substitution.
0005 Cost of Sales Accounting: This callup point is used for functional area substitutions
On the next screen add a description. To add a step to substitution, click on insert entry button. Specify of you are using a user-exit or select the field you wish to substitute. For field substitution, you need enter the following
Perquisite: The perquisite uses Boolean logic to determine if a condition is true. If the condition is true, the substitution is carried out. If the condition is not true, no further processing occurs. The valid Boolean logic operators are =, <, > and <>. The entry immediately following the Boolean statement must be put in single quotation marks unless a set is being used. Sets group together of a number of entries. When you use sets, the system needs to match only one of the entries. When you use sets, the system needs to match only one of the entries in the set for the prerequisite to be true. Sets are defined using Report Writer. The creation of sets will be covered later in this section. To link multiple logic steps together, either an AND or an OR is required at the end of each statement line.
Substitutions: This is the section where you tell the system what values to replace. You have the option of either using constant values or using a user-exit to specify values or carry out other logic statements.
Validations and substitutions are case sensitive – make sure you type in all your logic in CAPS – Check syntax does not find errors in small case.
Run the check syntax function to see if the Boolean logic has errors. Saving creates the ABAP code run your substitution.
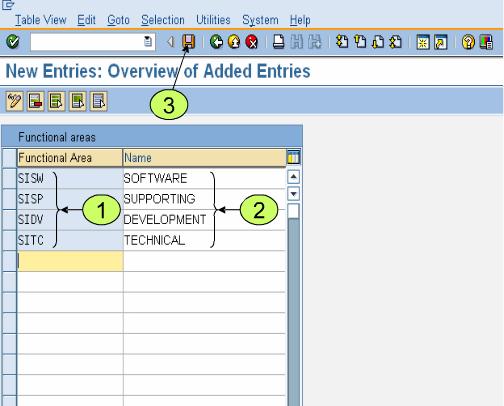
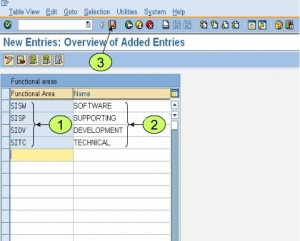
Maintain Functional Areas – OKBD
Functional Areas within the FI Enterprise structure are used to organize your business for cost of sales (COS) accounting. Functional areas allow you to segregate and classify different types of costs within one expense account. This makes it possible for example, to use a single labor account to determine what amount of labor is spent directly on production as opposed to sales or administration. It is possible to report on functional areas from both FI and Profit Center Accounting.
Enterprise Structure >> Maintain Structure >> Definition >> Financial Accounting >> Maintain Functional Areas
Transaction code: OKBD
Saks Apparel has determined that it requires five functional areas to classify cost of sales accounting. The functional areas are Administration, Sales, Production, Research & Development and Marketing. By using these functional areas, Saks Apparel will be able to report on an individual expense account using these five categories. Our next piece of configuration will be able to enable SAP to populate our postings with functional areas.
Activate FI Validations – OB28 or GGB4
FICO Configuration Series – Part 11
Activate Validations
Financial Accounting >> Financial Accounting Global Settings >> Document >> Line Item >> Define Validations for Posting
Transaction Code: OB28 or GGB4
OB28 takes you specifically to the FI validation application area. Using GGB4, you can manage the activation of all validations in the system for any application area or callup point.
CC: Four digit character identifier company code you want to activate your validation with. Only one validation can be active per company code per callup point. You can add additional steps to your validation in order to carry out more validations.
CallPnt: Enter the callup point you want your validation to be executed with.
Validation: Enter the identifier of the validation that you want to activate
Activtn Level: Enter the activation level for validation. Valid values are 0 (not active), 1 (activated throughout the system) and 2 (activated except for batch input)
Define FI Validations – GGB0
FICO Configuration Series – Part 10
Define Validations
Financial Accounting >> Special Purpose Ledger >> Tools >> Maintain Validation/Substitution/Rules >> Maintain Validation
Transaction code: GGB0
Validations are used to check settings and return a message if the prerequisite condition is met. You can use validations to supplement existing SAP logic to fit your business needs. A validation is valuable tool that can be used in many of the financial and controlling modules. In this section, we will configure an FI validation to fulfill our requirement of allowing postings from one particular company code to be posted only one particular business area.
In the screen follow the menu path (Validation >> Create) and enter the Name of validation, application area and callup point. The available options are as follows:
|
Option |
|
|
AM |
Asset Management |
|
CO |
Controlling |
|
FI |
Financial Accounting |
|
GL |
Special purpose ledger |
|
JV |
Joint Venture Accounting |
|
KC |
Enterprise Controlling (only Substitutions) |
|
LC |
Legal Consolidation |
|
MC |
Management Consolidation |
|
PS |
Project System |
Callup points determine when the validation is run. The callup points that are available are dependent upon the application area that is selected. For the FI application area, the following callup points are available:
|
Callup Point |
|
|
0001 |
Document Header: entries are stored in BKPF table |
|
0002 |
Line Item: Entries are stored in BSEG table |
|
0003 |
Complete Document |
In the next screen, enter the description of the validation and then click the insert entry button to add a step to the validation. Enter the prerequisite and checks using Boolean logic. The message is also typed in/selected after defining them as Error(E), Warning(W), Cancel(A) or Information(I). After all the details have been typed in, click the check syntax icon. Saving the validation generates ABAP code to perform the validation.
Business Areas – OX03
FICO Configuration Series – Part 9
Define Business Areas (click here for short version with screenshots)
Enterprise Structure >> Maintain Structure >> Financial Accounting >> Maintain Business Area
Transaction code: OX03
The function of a business area is to create balance sheets and profit and loss statements below the company code level. Some common uses of business are to produce divisional financial statements or SEC segment-level reporting. It is important to note that business area functionality can be duplicated using profit center accounting. The decision to use or not to use business areas should be made early on in the design phase of your project. Many new projects are leaning away from business areas and towards profit centers, but ultimately, the decision is an individual project decision based on what fits in the overall system design of the project implementation. Some of the deciding factors are the need to report business lines across company codes, the need for full balance sheets at the divisional or business line level, as well as the cost and the benefits of business areas versus profit centers.
Business areas are independent of any other FI enterprise structure. Therefore, business areas are designed to cut across company codes. A common mistake that some companies make is to force one-to-one relationship defeats the entire purpose of business areas. The purpose of business areas is to be able to report on similar activities that occur across company codes. There is no residual benefit to configuring business areas in that manner. As a matter of fact, it often causes a lot of reconciliation problems because business areas are not linked to company codes in standard configuration.
In this screen enter Alphanumeric identifier for the business (up to 4 char) are and description
Saks Apparel has decided to use three business areas. The CFO has determined that he would like a cross-company balance sheet for both the apparel and textile industries in which Saks Apparel conducts business activity. In order to better track non-value-added administrative assets and expenses, the services business area was created. The new shared services department that provides centralized administration functions for the organization is being implemented as part of the business process reengineering effort portion of the SAP project implementation. It is important to remember that the idea is for all company codes to share all the business process reengineering effort portion of the SAP project implementation. It is important to remember that the idea is for all company codes to share all the business areas. The one exception is that the accounting department wants to ensure that postings one particular company code are only posted to one particular business area.
Although Business Areas are not linked to any other FI Enterprise Structures, they can be linked to other organizational elements in the system. Some of them are listed below:
|
Enterprise Structure |
Why is this linked to the Business Area? |
|
Plant/Valuation Area & Division |
Very useful to link Business area to plant/valuation area and division because single plants usually produce products for one Business Area |
|
Plant & Division |
Similar to previous. The decision whether to link or not is taken by the MM team |
|
Sales Area |
In sales organizations which sell a single grouping of products, business areas are linked to sales areas to ensure revenue postings are made to correct business area |
|
Cost Centers |
Sometimes, it makes sense to map business areas to cost center |
|
Assets |
In the company code, if the Business Area Balance Sheet indicator is enabled, business area becomes a required field fixed asset class module |
|
Consolidation Business Areas |
Consolidate business areas for reporting purpose |
Define Parallel Currencies – OB22
FICO Configuration Series – Part 8
Define Parallel Currencies
Financial Accounting >> Financial Accounting Global Settings >> Company Code>> Parallel Currencies >> Define additional local currencies
Transaction Code: OB22
Company Code: Enter the four-digit identifier of the company code that you wish to configure.
1st Local Currency: These fields will fill in automatically with default information based on the currency defined in the company code definition.
2nd and 3rd Local Currency: As explained earlier, each company code can have two additional parallel currencies that can be used in conjunction with local currency defined for the company code
Curr. type: The currency type field specifies which type of parallel currency you want to configure. The following options are available.
Group Currency: Group currencies are defined at the client level in table T000. Group currencies are used to enable cross-company postings in controlling for company codes that use different company code currencies.
Hard Currency: Hard currencies are used for subsidiaries in countries with a lot of inflation. Hard currencies allow you to better valuate transactions in an inflationary economic environment.
Index-Based Currency: Index-based currencies are used for statutory reporting purposes for subsidiaries in some countries that have extreme amount of inflation.
Ex. Rt. Type: The exchange rate type determines how foreign currencies are revalued at the time of foreign currency revaluation and translation. The number of possible entries is too numerous to list here J
Srce Curr: Enter the source currency that the foreign currency is to be translated against. The possible entries are as follows:
Translation taking transaction currency as basis: This option always tries to translate the parallel current against the transaction currency of the document.
Translation Taking First Local Currency as Basis: This option always translates the parallel currency against the first local currency (company code currency).
TrsDte Typ: This setting is used to determine which date is used for foreign currency translations. The available options are as follows:
1. Document Date: Select this option if you want the translation calculation to use the exchange rate that was In effect on the day the document was dated.
2. Posting Date: Select this option if you want the translation calculation to use the exchange rate that was in effect on the posting date in the document.
3. Translation Date: Select this option if you want the translation calculation to use the exchange rate that is in effect on the date of the foreign currency translation.
Saks Apparel has decided to use a hard currency to help offset the inflationary pressures of its Mexican based company code. US dollars are used as hard currency. The peso is the company code currency for the Mexican division. Saks Apparel has decided to use the transaction currency as the base currency for translation and to use translation date to determine proper exchange rate. Because we have company codes with different currencies using the same controlling area, we also configured a group currency of US dollars for all company codes. The group currency will allow us to make cross company code postings in the controlling module. We will also need to make entries for all of the US company codes to add the group currencies to their records.